
They can be traced to the jyā and koṭi-jyā functions used in Indian astronomy during the Gupta period. a law stating that the square of a side of a plane triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice the product of the other.
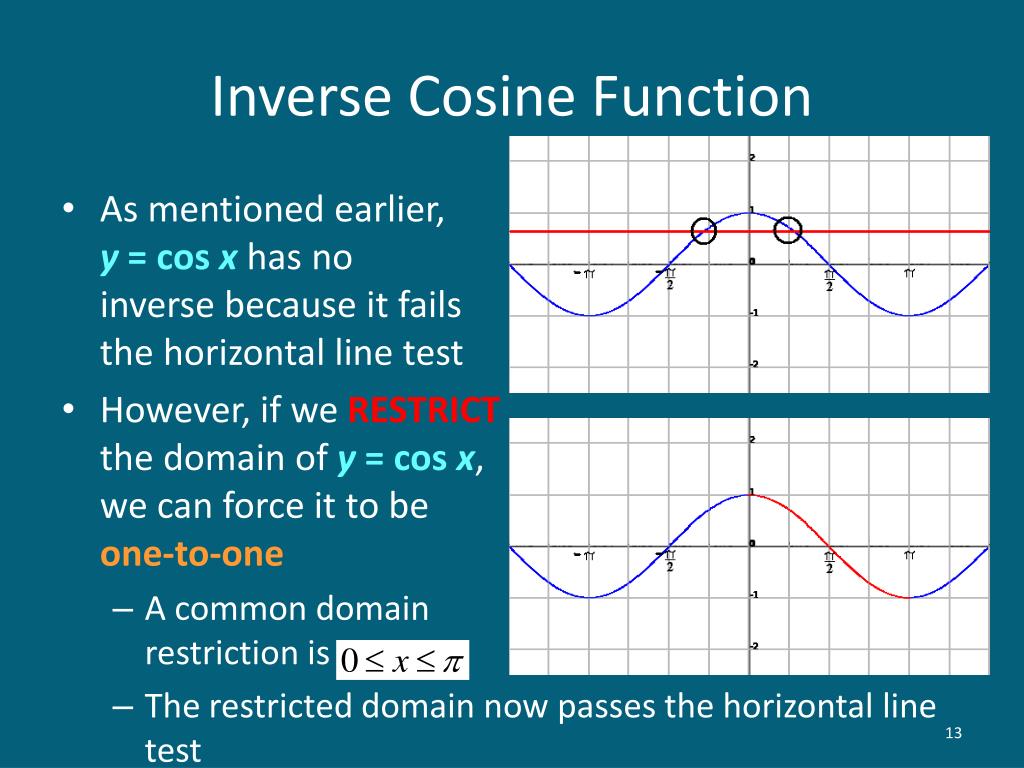
The sine and cosine functions are commonly used to model periodic phenomena such as sound and light waves, the position and velocity of harmonic oscillators, sunlight intensity and day length, and average temperature variations throughout the year. Law of cosines c2a2+b2-2abcos (gamma) c2 a2 +b2 2abcos() Want to learn more about the law of sines Check out this video.
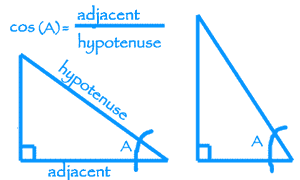
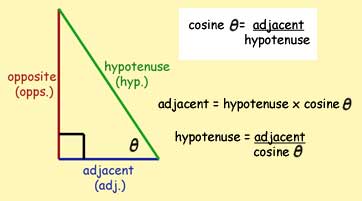
More modern definitions express the sine and cosine as infinite series, or as the solutions of certain differential equations, allowing their extension to arbitrary positive and negative values and even to complex numbers. More generally, the definitions of sine and cosine can be extended to any real value in terms of the lengths of certain line segments in a unit circle. They are useful for finding things like shortest distances and equations of. If you want to use degrees instead of radians, you have to convert. , the sine and cosine functions are denoted simply as Directional cosines are a way of describing lines in space in terms of ratios. s(x) returns the cosine (a value between -1 and 1) of the angle x (given in radians). The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle (the hypotenuse), and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. Cosine Cosine, written as cos (), is one of the six fundamental trigonometric functions.
Wikipedia Rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
